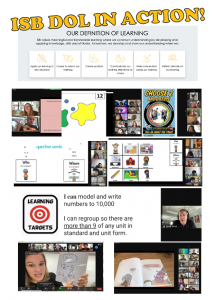
The ES vice principals, Ms. Sarah Fleming and Mr. Jeff Scott, and I share a common ongoing goal to visit classrooms as much as possible, and we have made it a priority to visit every virtual classroom using ISB’s Definition of Learning as a lens for the observations and personalized feedback to teachers these past two weeks. During our many hours in the virtual classes we saw a plethora of excellent instructional strategies aligned with the ISB Definition of Learning (pictured below).
Some highlights we observed and shared with ES faculty earlier today included the following:
Apply our learning to new situations
- In Art, students are applying their observational drawing skills, noticing lines and shapes, to sketch their hands in different positions.
Inquire to extend our learning
- Some grade levels are launching narrative writing units where students have the opportunity to self-reflect and begin to inquire into possible topics they might want to explore for their own pieces of writing. The self-generated topics and “seeds” are based on their own experiences, character traits, and life-lessons they want to inquire into further.
- PreK students are exploring different ways of sorting materials and considering why they sorted in that way.
- In music, students are thinking about the meaning of words (eg. membranophone, aerophone, idiophone) using similar word inquiry strategies to those in the core learning areas!
- Students are learning to use sentence stems to approach mathematical learning experiences with a sense of curiosity and interest ie. I notice….. I wonder…
- Students have been learning lessons from mentor authors about how to communicate meaning through illustrations.
Create solutions
- Providing ample choice for students to self-organize, self-monitor and make choices that drive their learning.
Communicate our learning effectively to others
- Students explaining their thinking and reasoning in mathematics.
- Many teachers are using different strategies to support student-to-student connections in virtual school such as Think-Pair-Share breakout rooms.
- Many strategies for monitoring engagement – calling on students to participate and confirm their understanding of directions, using the chat feature for formative data, having the accountability of having their cameras on.
Make connections across our learning
- Students are explicitly reflecting on the ISB attributes and how they apply across all areas; many teachers have been making connections to the self-managing attribute during the launch of the school year
- As new concepts are introduced in Math (ex: exponents), students are being prompted to activate their prior knowledge, and connect it with concept they have developed in previous grade levels (ex: multiplication, place value
- Students are learning how to draw upon their background knowledge when reading.
Reflect critically on our learning
- Students are providing feedback to each other on their memoir writing via a guided “glow” and “grow” process. Explicit teaching regarding how to give and receive constructive feedback was incorporated into the mini-lesson.
- Overall we saw less evidence of this particular aspect of our Definition of Learning with students; however, in the responses we got from teachers to our written feedback, we noted many examples of teachers exhibiting high consciousness, reflecting on their practice, and considering adjustments.
Our students and teachers are all doing their very best to ensure that students continue to make gains towards our defined learning goals and outcomes. As you observe your children’s growth and development during these days of virtual school, we invite you to consider how the ISB Definition of Learning is impacting your child.
Your partner in education,
Michael Allen
michaela@isb.ac.th